
Instructions for working with XML sitemaps
In order for the site pages and the content to be ranked (displayed at the request of users), they must be indexed by the search engine robot. When a resource has a sitemap, it's easier for Google to discover page addresses.
What is a sitemap
A sitemap is a file containing a list of the URLs of all the pages of a resource that need to be indexed. It is located in the root folder and in most cases is called XML sitemap.
The structure of the site resembles the structure of a book with sections, subsections and pages. When a reader needs to find something in a textbook or encyclopedia, he first looks at the content table and finds the right page. An XML sitemap acts as the content table of a website, helping search engine crawlers discover pages.
How to view the sitemap
The content of the site map is available not only to robots, but also to site visitors. Since the list of URLs is usually placed in the folder with server files, the sitemap address consists of two elements, the name of the site and the name of the map.
How to view a map of someone else's site? Let's take Apple's website as an example and add /sitemap.xml to the domain name in the address bar.
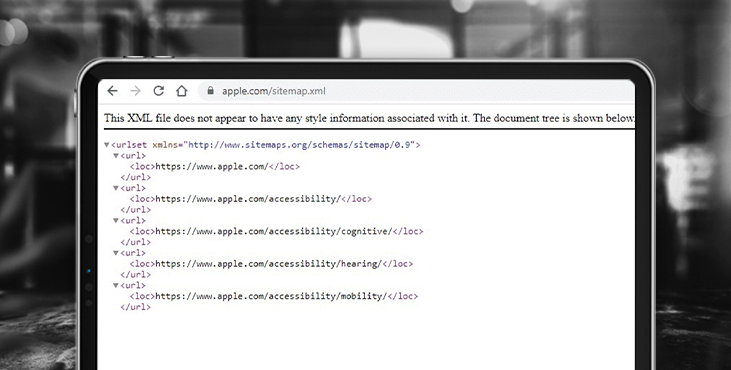
What is a sitemap used for?
The main role of the sitemap is to navigate the robot and direct it to important URLs so that they get into the search engine index. It is important to note that the presence of a map does not guarantee page indexing. Also, search engines can find a URL without a map, for example, if a link leads to it from another web page. At the same time, Google recommends adding a list of addresses for indexing to your site.
Like robots.txt page crawling instructions, a sitemap is an important optimization attribute. You can check the correctness of the sitemap settings in tools from search engines, on validating sites and on platforms that analyze the site's SEO online.
When a sitemap is useful:
1. The site has many pages
Imagine a large online store or other multi-page site. With a large number of pages, the robot may skip some of them. A sitemap increases the likelihood of important URLs getting indexed and, as a result, appearing in SERPs.
2. New website:
In order for a new resource to start ranking, you need to help the search engine find its pages. If the URL is not mentioned on other pages on the Internet, it will be more difficult for the robot to find this URL and index it.
Creating a sitemap and informing crawlers about its availability will speed up the indexing of pages and their display by search queries.
3. Website content is constantly updated:
For a site that is already in the index, it may also be important to speed up the indexing of pages. For example, news and entertainment portals are constantly adding new articles and are interested in the fact that users can quickly find fresh materials in the search results.
Also, the map may indicate the date of the last page update or the frequency with which it is updated. In this way, the robots receive information when it is necessary to re-index the URL.
4. Certain URLs are not linked from other pages on the site.
Typically, pages within a site are linked to each other. For example, the main page contains links to product categories, category pages contain URLs to product cards, product cards can link to a page about payment and delivery.
When the robot finds links on a page, it can follow them, gradually crawling more and more URLs. If the address is not related to other pages of the site, the crawler will be able to find it thanks to the sitemap.
5. The site has a lot of images and videos
Not only site pages, but also their individual elements can participate in the ranking results. For example, Google has sections where only images or videos are displayed.
Pictures and videos that the user sees on the site look like links to files in the page code. The browser accesses these links to media files and displays visual content on the screen. If you create a separate map for such URLs, this will draw the attention of robots to this type of content.
How to create an XML sitemap
The XML file can be obtained using tools that automatically generate a list of URLs based on site pages, or manually mapped.
Automatic sitemap generation.
There are several ways to get an XML sitemap ready.
1. Online services for creating files. These are services that generate files and feeds by site URL, including sitemap. To start the generator, specify the domain name in a special window. In a few minutes, you will be able to download the finished XML map.
2. Plugins for content management systems (CMS). CMS developers offer additional programs for SEO settings, including a sitemap. The plugins automatically create an XML sitemap file and update the list of URLs when you add or remove pages.
The sitemap file creation
Since there are automatic services, there is usually no need to manually list pages. But if you still want to create a sitemap by yourself:
1. add a file with the XML extension to the root folder on the hosting;
2. list all the URLs that the search engine should index according to the syntax and general rules for a sitemap.
Sitemap file creating rules
Let's highlight the general recommendations of search engines for creating a sitemap.
- The allowed number of links in the map is up to 50,000, and the maximum sitemap size is no more than 50 MB.
- The link must not be longer than 2048 characters.
- All URLs must start with http or https.
- Links must be in UTF-8 format.
- In addition to XML, another sitemap format is acceptable, for Google, this is a TXT, RSS, mRSS and Atom 1.0 file.
- The sitemap should contain only canonical URLs, the pages marked as priority from several similar ones. This is true for sites that have copies of pages to prevent duplicate content from getting into the index.
- A link to a sitemap can be specified in the robots.txt file, which is an instruction for robots to view before crawling a resource.
- The list of URLs must not contain pages with a noindex tag that disables indexing.
- The list of URLs should not contain pages that are not allowed to be crawled in the robots.txt file.
How to place a sitemap in a robots.txt file
Before adding pages to the index, the robot first crawls the site. The first file it looks at is robots. You need to add the Sitemap directive and a link to the sitemap to it.
The robots file can contain links to several XML files.
What does a sitemap consist of?
The sitemap file consists of elements - tags that have a beginning <> and an end and contain certain data. Some tags can be parent tags and include child tags. The sitemap syntax for Google follows the Sitemap protocol.
The XML map has the required tags:
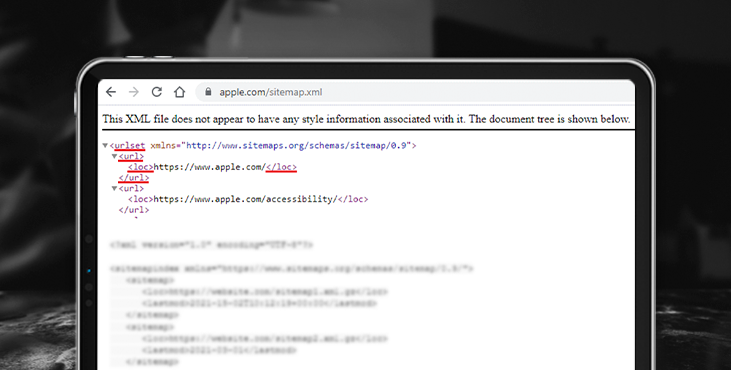
Now consider the tags that are used if necessary:
Google mentions the
How to add multiple maps to a site
If the site has several sitemaps that you need to report to search engines, use one of two options for this:
1. the robots.txt file, which contains links to maps using Sitemap directives;
2. XML sitemap file containing links to all the sitemaps.
Let's consider step by step the second method combining several maps in one file.
STEP 1 Create XML files and check that the total number of URLs does not exceed 50,000 and the weight is 50 MB. STEP 2 Give the files names other than sitemap. STEP 3 Check cards for errors using special tools. STEP 4 Create an XML sitemap file and add links to all maps inside the parent
Example sitemap.xml containing two sitemaps:
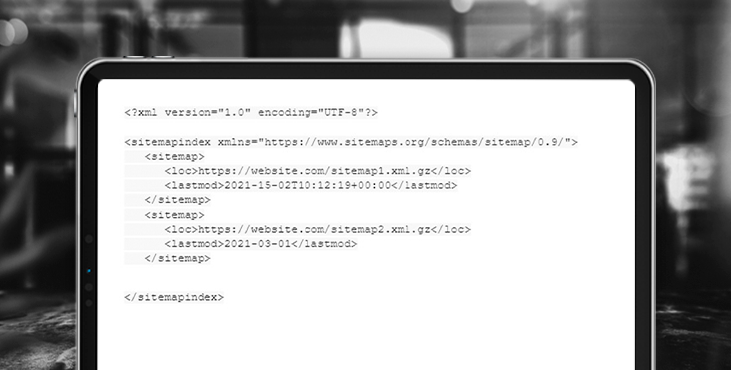
The gz extension indicates that sitemaps have been compressed with gzip.
In order for search engines to find all "nested" sitemaps, it is enough to notify them about the main sitemap.xml file through a special tool, for example, Google Search Console.
Sitemap for different types of content
In order for the content of the pages to fall into special sections of search engines (for photos, videos, news), it is recommended to create separate sitemaps.
Sitemap for images
When to use an image sitemap? There are a lot of images on the site and well you need to help the crawler not to miss the important ones;
It is difficult for a search engine to find links to photos, for example, if they appear on the screen as a JavaScript element.
An image sitemap consists of
Required tags:
Optional tags:
Sitemap for video
If you need to notify Google of recently added videos or help it index a site with a lot of multimedia content, use a video map.
A video sitemap is similar in structure to an image sitemap. Information about files is placed in the parent
Required tags:
Optional tags:
Sitemap for multilingual sites
If the site has several language versions, the sitemap should include page addresses in other languages. To do this, use the rel=”alternate” and “hreflang'' elements. They inform the robot that the page has a different version and tell the page's language in the standard format: en, ru, it, de.
Thus, the search engine not only indexes the pages, but also displays their versions in the results depending on the user's language.
How to set up a sitemap for a site with language versions
Add a child
Example:
rel="alternate" hreflang="en" href="https://website.com/english/page.html"/> Here we see the URL of the page specified in the If the site has a map, it is worth notifying search robots about it. Google has a service where you can upload a sitemap and submit the map to a search engine. This will speed up the indexing of pages. To add a map, go to Google Search Console and verify the rights to the site using one of the suggested methods. If you have access to the service, go to the "Sitemaps" tab, enter the name of the XML-map in the form and click "Submit". Let's talk about tools that analyze how well files are composed. In the "Sitemaps" section, under the line for submitting the map, you can see the status of the review. A valid sitemap will have a "Success" status. The SE Ranking service performs a comprehensive SEO site audit, including XML map analysis. The "Scanning" block contains the results of checking the sitemap file: whether the site has a map and whether its size corresponds to the norm. It also displays errors related to the presence of non-canonical URLs in the list, pages in the code of which there is a prohibition of noindex indexing, or those links that are prohibited from crawling in robots.txt. Website Planet has a handy sitemap validator. It prints out the total number of URLs in the map, file size and errors. A sitemap helps search engines find and index pages on a site. Using an XML file, you can influence whether content is included in the index and, as a result, the ranking results. Having a sitemap does not guarantee, but greatly increases the chances of important pages being indexed. The XML sitemap file can contain not only URLs, but also additional information about them: indexing priority, update time, availability of language versions. One site can have several maps, including separate sitemaps for images, videos, news. Get an SEO Analysis for your website as a bonus By clicking 'Submit', you agree to Privacy Policy and authorise our staff to contact you. You are liable under the Personal Data Protection Act if you key in false personal data or other people’s personal data.How to make the sitemap visible to Google
How to check sitemap XML for errors
Google Search Console
SE Ranking
Website Planet
Conclusion
Tell us what you think
offers and news
