
What is SSL certificate and how it affects SEO
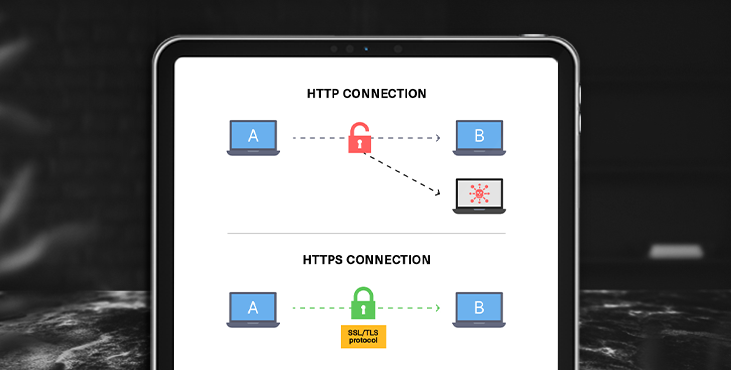
Any action on the Internet is an exchange of information between browsers and servers. At the same time, they initially communicate through the operation of the HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol). But this protocol does not encrypt data, which is not safe when it comes to transferring personal information. Not only logins and passwords, but also bank card numbers, account details, passport details, etc.
To protect such information, HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol Secure) was created. It works for sites that have a kind of digital signature, or connection key, that is, an SSL certificate. This certificate certifies the authenticity of the site.
When a connection is established, the browser requests a key-certificate and checks the received data with the certificate authority. Having verified the legality of the document, the browser considers the site with the certificate safe and establishes an encrypted connection with it.
This is a guarantee that the transmitted information will not be seen by third parties (scammers, hackers) even if they intercept the data, they will not be able to decrypt it. All information remains known only to the user and the server.
SSL in the name of the certificate is an indication of the Secure Sockets Layer protocol. It processes the data that websites exchange with each other and encrypts them so that scammers do not receive confidential information. At the same time, the HTTPS protocol is responsible for the completeness of the transmitted data - it guarantees their transmission without loss.
The presence of an SSL certificate on the website is demonstrated in the browser line: in front of the web address there is an image of a closed padlock.
Information included in the certificate:
- validity period (end date);
- signature algorithm, encryption;
- domain name of the web resource;
- information about the owner;
- information about the certification authority where the document was issued, etc.
Certificates are divided into 3 groups according to the signing source:
1. Self-signed. Issued to everyone upon request. Essentially useless as modern browsers, when visiting sites with such certificates, issue a warning that the connection is not secure.
2. Signed by untrusted certificate authorities. Genuine documents issued by organizations not trusted by browsers.
3. Signed by trusted certificate authorities. These are validated data certificates issued by trusted organizations that display correctly in all browsers.
Certificates issued by trusted certification authorities, in turn, come in various forms. They can be issued to individuals and (or) legal entities for one domain, a domain with subdomains, or a group of domains. At the same time, in various ways (via email, DNS records, server hash files), they check domain ownership, check owner data, etc.
The more functions a certificate has, the more efficient it is in operation, but its cost also changes accordingly.
Who needs an SSL certificate for a website and why?
It is clear that certificates are important for web resources on which financial transactions are carried out. In addition, the safety of information is necessary on sites where other personal, especially confidential, data is exchanged.
Thus, owners cannot do without certificates:
- online stores;
- corporate sites with payment systems;
- websites of legal, financial organizations, payment services, etc.;
- social networks.
It may seem that information sites that create content and do not work with personal data do not need to install an SSL certificate. However, it is not.
SSL certificate and SEO
There is a connection between the presence of a certificate at the site and its position in the issuance of search engines. Back in 2014, Google officially announced that the presence of the HTTPS protocol is a feature that is taken into account when ranking, and introduced the indexing of the corresponding pages. It was after this that http sites began to be marked in browsers as unprotected, and sites with security certificates became easier to move up to the TOP.
Accordingly, the attitude of users has also changed as now they trust resources that guarantee the protection of their personal data much more. For a part of the user audience, even the security of ordinary web surfing is important, during which they do not use information about themselves anywhere.
Browsers notify users that specific sites are not secure, and search engines rank such sites poorly. As a result, web resources with SSL certificates rise higher to the TOP of issuance. That is, the presence of a certificate affects the behavioral factors of a web resource.
If you look at the TOP results for any competitive query, you can see that the first page is dominated by web resources with a secure protocol.
In addition, HTTPS significantly increases website loading speed and also protects users from aggressive advertising. It can appear on insecure sites if you access them, for example, using free Wi-Fi at a gas station or in a shopping center and causing a decrease in browsing depth.
Therefore, more and more website owners either buy a certificate immediately when creating a web resource, or switch to the HTTPS security protocol so as not to lose the target audience.
Certificate selection
Which certificate to choose depends on the type of project and the specifics of data transfer via a secure protocol. There are many options available:
- to transfer one domain to HTTPS (a classic option for companies and individuals);
- for sites with subdomains or child subsites;
- for a group of domains (especially with a simultaneous transition);
- for websites with billing systems, resources of financial organizations.
Pros and cons
The key benefits of connecting a strong SSL and switching to HTTPS for SEO and in general:
1. You get protection from fraudsters intercepting and replacing user data (reducing the likelihood of getting into an unpleasant situation in connection with such an incident).
2. You get the opportunity to easily identify and confirm your rights to the domain (for legal entities).
3. You increase the level of trust of users from your target audience, who are not afraid to enter addresses, passwords, data for paying for products on the site.
4. Maintain and increase traffic (and often conversions) on the site.
5. You get a chance to raise your site higher in Google search results.
6. Improve your statistics. It has been noted that traffic for web resources that use the secure HTTPS protocol and link to resources that do not use it is considered not referral, but direct.
There are very few disadvantages of transferring sites to HTTPS and even those are not so much disadvantages as minor inconveniences:
1. The certificate must be paid annually (however, the amount depends on the properties of the certificate and is quite acceptable for most site owners);
2. When moving, the site will need to be configured, which takes time.
The opinion that buying an SSL certificate negatively affects SEO success (traffic drops) and website position is wrong. Of course, after the move, search engines may perceive the web resource as a completely new one, but only if you entrust the move to a non-professional who cannot correctly configure all the parameters. So it is better to choose a professional SEO team for your project and save your time.
Get a free web development consultation
Tell us what you think
By clicking 'Submit', you agree to Privacy Policy and authorise our staff to contact you. You are liable under the Personal Data Protection Act if you key in false personal data or other people’s personal data.
offers and news
